5G is the fifth-generation of cellular
technology that is generating new innovations to transform wireless
communications. This technology is being incorporated into radio, the core network in telecommunications, cloud services,
user devices and information processing through the edge computing. 5G technology
presents a unique capability that
has the potential to disrupt.
The Big Picture
The technological advances sweeping the world today can be compared to the mid 20th century revolution triggered by the inroads made by electronic
& IT, preceded by division of labor and mass electrification lead expansion of industrial production in
the late 19th century, preceded by the steam lead mechanization in the mid-18th century1. Modern
advancements in communication and connectivity have led to the Fourth Industrial Revolution or 4IR.
This shift will result in sweeping technological, socioeconomic, and cultural
changes that will redefine the way we live.
5G mobile communications has the potential to play a key role in this next industrial revolution.
The earlier generations of
cellular technologies, 4G and 3G, demonstrated the ability to bring digital penetration
and deliver a multitude of
services while keeping the complexity of the technology hidden from consumers. 5G extends
these very characteristics of
simplicity to a user while bringing
in a completely new set of underlying capabilities.
Reimagining
products and services
It
is imperative for all
stakeholders that are part of the 5G landscape,
governments, and enterprises
collaborate and explore various possibilities and synergies in
order to leverage the power of 5G. While there have been
many successful field trials with actual rollouts, the most effective use cases
for 5G are still
unclear2. These potential
applications can be understood
with existing 3G/4G networks while some are better suited for a WiFi type private network. In other situations, wired broadband
is a better option. Similarly, there are more suitable network options in many IoT applications.
The process of identifying targeted
vertical and horizontal use cases
should involve taking a larger
system level view, synthesizing the products
or services constituting it, and potentially exploring
the elements adopting 5G features.
Merriam-Webster defines a system3 as
"a regularly interacting or interdependent group of items forming a unified
whole," such as "a group of devices or artificial objects or an organization
forming a network especially for distributing something
or serving a common purpose."
Figure 1.

Exploring
possibilities with the larger
system level view and applying proven methodologies like "System Thinking" will help test the present boundaries of a system, break
away from convention and look at many closed-systems as open-systems in the future.
A
potential use case
Let
us explore a scenario involving concerts. A lot
of planning and money goes into delivering a hightech experience to a live audience. Several systems are used to
deliver a holistic experience including video, audio, stage lighting, security and surveillance,
as well as external systems
outside the venue. Setting up the equipment is a major task involving
specialized skills, tools and resources. Getting the right amount of cables and
interconnecting them to specification is a complex process. Technical and
non-technical restrictions on laying cables and meeting prerequisites for
assembly require specialized
skills to accommodate different
venues. Overall, cables are always
a logistical nightmare and can
add on additional costs for manufacturing and shipping the products.
Below
is a simplified representation of the setup
required for a live performance. Some of
the elements are much larger in number.
Figure 2.
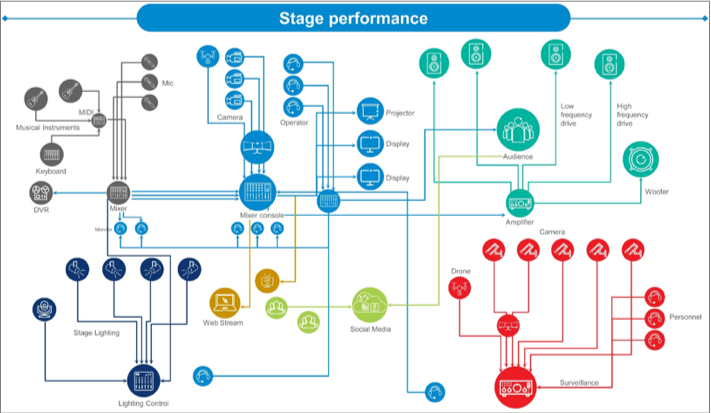
There are various
systems involved in a stage performance.
These systems are often are isolated and don't interact with the others. For example, the stage lighting does not interact with
the video systems and similarly
to the surveillance systems. We can take this composite system to the drawing board to analyze the individual
systems being used and test the physical
and logical boundaries of each
system. That's where 5G technology
comes in as an external
communication system. This as an alternative to every physical wire that is used to
interconnect discrete system
components here.
Figure 3 illustrates a 5G-enabled wireless world allowing an
almost cable-free stage performance.

Product
manufacturers need to gain the necessary
hardware to incorporate 5G technology
into their products to enable D2D (Device to Device) or cell-based
communication. This feature will
command a premium for the product as this indirectly results in significant
savings for the customers. In
addition to the business case,
some of the pros and cons like the ones
below have to be evaluated by the stakeholders.
Figure 4.

Systematic exploration can unearth many valuable use cases
for 5G. After carefully weighing the risks and rewards, the scope, scale and pace of adoption can be decided. Considering the money and reputation at stake, it is
critical to first explore and test 5G technology
in smaller events and conferences
with fewer complexities.
##
About
the Author
Saji
Thoppil - Chief Technologist - Cloud and Infrastructure
Saji
Thoppil is the Chief Technologist
for Cloud and Infrastructure at
Wipro. He drives the Edge Computing charter under Wipro's 5G initiative.
Use cases and lifecycle management are his focus areas. Saji
is in the governing board of
LF-Edge & Oasis TOSCA.
He has 25+ years of IT industry experience encompassing design, build and
operationalization of complex, distributed IT systems. In recognition of his
contribution to the organization
and the industry, he was conferred the title of Wipro Fellow - Distinguished Member
of Technical Staff. During his distinguished career, he has created multiple practices and incubated several new
IPs for Wipro. Wipro's Fluid State Data
center designed and developed by Saji was one of
the industry's first blueprint
for converged infrastructure. He is
also the architect of deployed
Wipro's first public cloud which was one of
the first public clouds to go live in
the Indian sub-continent.
Bibliography
- Davis,
Nicholas. "What Is the Fourth
Industrial Revolution?" World Economic Forum, 19 Jan. 2016, www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/01/what-is-the-fourth-industrial-revolution/.
- Bleicher,
Ariel. "First Intercontinental 5G Trial Begins at Winter Olympics." IEEESpectrum: Technology, Engineering, and Science News, IEEE Spectrum, 21 Feb. 2018,
spectrum.ieee.org/tech-talk/telecom/wireless/first-intercontinental-5g-trial-begins-at-winter-olympics.
- Staff, Staff. "System |
Definition of System by Merriam-Webster." Merriam-Webster,
Merriam-Webster, 28 Apr. 2019, www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/system.